|
|
|
 |
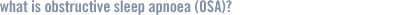
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea is a serious, potentially life-threatening
condition that is far more common than is generally understood.
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea is a breathing disorder characterised
by brief interruptions of breathing during sleep. It owes
its name to a Greek word, apnoea, meaning "without
breath".
The effects of OSA is that a person can stop breathing
for periods when asleep. These interruptions (apnoeas),
which last for 10 seconds or more, occur when the airway
narrows so much that it closes. This stops breathing, and
the brain reacts by briefly waking the subject, causing
the airways to re-open and breathing to restart. The individual
is usually unaware of this awakening and this process can
be repeated up to several hundred times during the night.
Proper restful sleep becomes impossible, resulting in sleepiness
and impairment of daytime function. Early recognition and
treatment of OSA is important. The excessive sleepiness
associated with OSA impairs quality of life and places people
at increased risk of road traffic and other accidents. It
may also be associated with irregular heartbeat, high blood
pressure, heart attack and stroke.
- "Apnoea" is a Greek word meaning "without
breath." An apnoea is clinically defined as a cessation
of breath that lasts at least ten seconds.
- "Hypopnea" also comes from Greek: "hypo"
meaning "beneath" or "less than normal"
and "pnoea" meaning "breath." A hypopnoea
is not a complete cessation of breath but can be defined
as a perceptible reduction in airflow that leads to sleep
fragmentation or to a decrease in the oxygen level in
the bloodstream.
- The apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI) or respiratory disturbance
index (RDI) refers to the total number of apnoeas and
hypopneas divided by the total sleep study in a patient’s
sleep study. The AHI gives one measure of the severity
of the sleep apnoea.
- Typically the soft tissue in the rear of the throat
collapses and closes the airway, forcing sufferers to
stop breathing repeatedly during sleep, sometimes hundreds
of times a night.
- Although the typical Obstructive Sleep Apnoea patent
is overweight, male, and over the age of forty, sleep
apnoea affects both males and females of all ages and
those of ideal weight.
The most common symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea are
loud snoring and excessive sleepiness (i.e., falling asleep
easily and sometimes often inappropriately). Untreated Obstructive
Sleep Apnoea can be life threatening; consequences may include
high blood pressure and other cardiovascular complications.
|
|